Electronically commutated (ECM) motors are
brushless DC motors where the direction of the electric current is switched using electronic controllers. As the switching of the current is technically known as "commutating", brushless motors are also called "electronically commutated" motors. ECM motors provide the advantages of brushed
DC motors in terms of the ability to have variable speed control, but without the drawbacks of brushes. Without brushes to wear out, ECM motors have design lives equal or longer than AC motors. GP ECM motors can be operated directly from AC mains supply (115V/230V/380V), or from DC(12V/24V/48V).
ECMmotor in HVAC Systems
When considering an ECM for application in an HVAC system, there are several factors to keep in mind. Although ECMs are often selected because many models run at variable speeds, in certain condenser applications it is preferable to select and ECM that runs at a fixed speed—an ECM running at a fixed speed s in a condenser unit still uses less energy than a typical
PSC motor running at a fixed speed in a similar unit. As a result of increased energy savings, a condenser operating with an ECM will have a higher SEER (seasonal energy efficiency ratio) rating. In other HVAC units, an ECM can run at variable speeds but depends on a controller that pre-programs speed, including the rate at which the motor ramps up. Whereas typical PSC
motors start and almost immediately run at full capacity, an ECM can start slowly and stop slowly, which can help reduce humidity. Additionally, the control can be set to alter the amount of air an ECM motor drives through the system, which enables a greater range of possible air-flow rates.
The specifications:
| Model | Rated Voltage (VAC) | Frequency(Hz) | Rated Speed (RPM)) | Speed control |
| 113-3/4hp | 240 | 50 / 60 | 1300 | 0-10V/PWM |
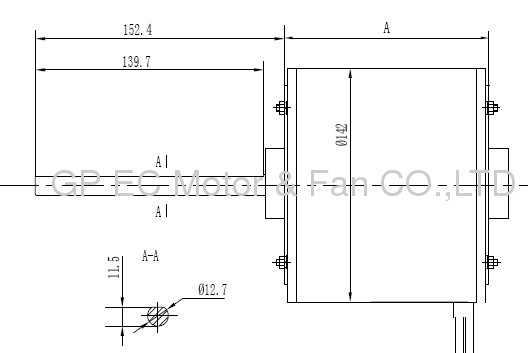
The outlines:
 ECM motor-Energy saving vs induction motor-PSC
ECM motor-Energy saving vs induction motor-PSC




